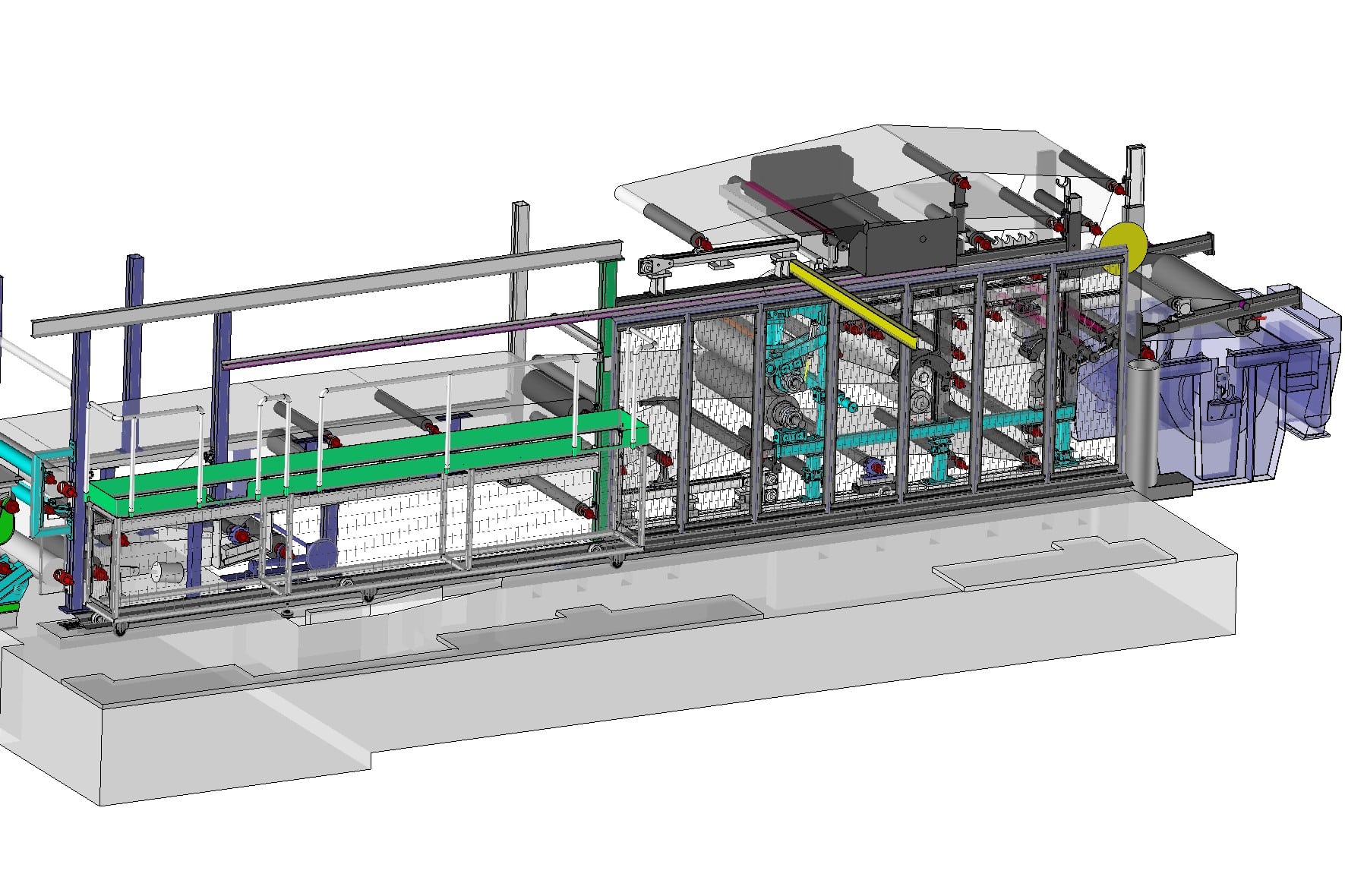
Software resources

CAD software, 3D Modelling software
TopSolid Design (8 licences)
Published by TOPSOLID, 2nd French publisher of CAD/CAM software.
- Design of parts and large mechanical assemblies
- Layout
- Kinematic
Créo (2 licences)
Published by the American company PTC
- Design of parts and large mechanical assemblies
- Layout

“If necessary, we can also adapt to other software. (Experience with Solidworks)”
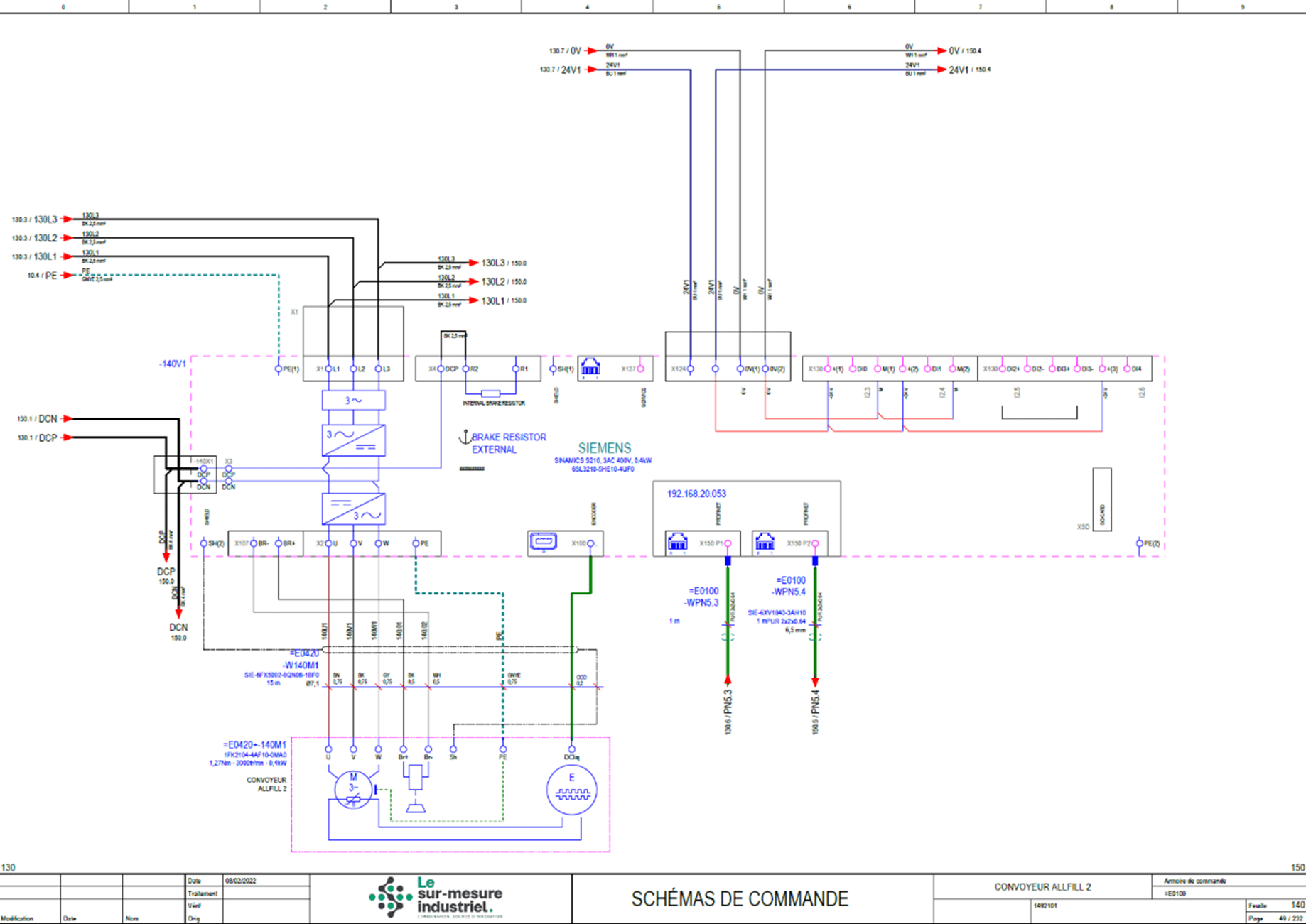
Automation, schematics, programming software:
- SEE Expert electrical schematic software, published by IGE XAO
- EPLAN electrical schematic software
- SIEMENS programming of programmable controllers, drives
- SCHNEIDER programming of programmable automatons, speed controllers
- TeamViewer, Etic: remote connection and control
Robotics:
STAUBLI SRS
Robot programming software
- 3D environment
- Trajectories
- Communication with the PLC
- Security management
- Simulation
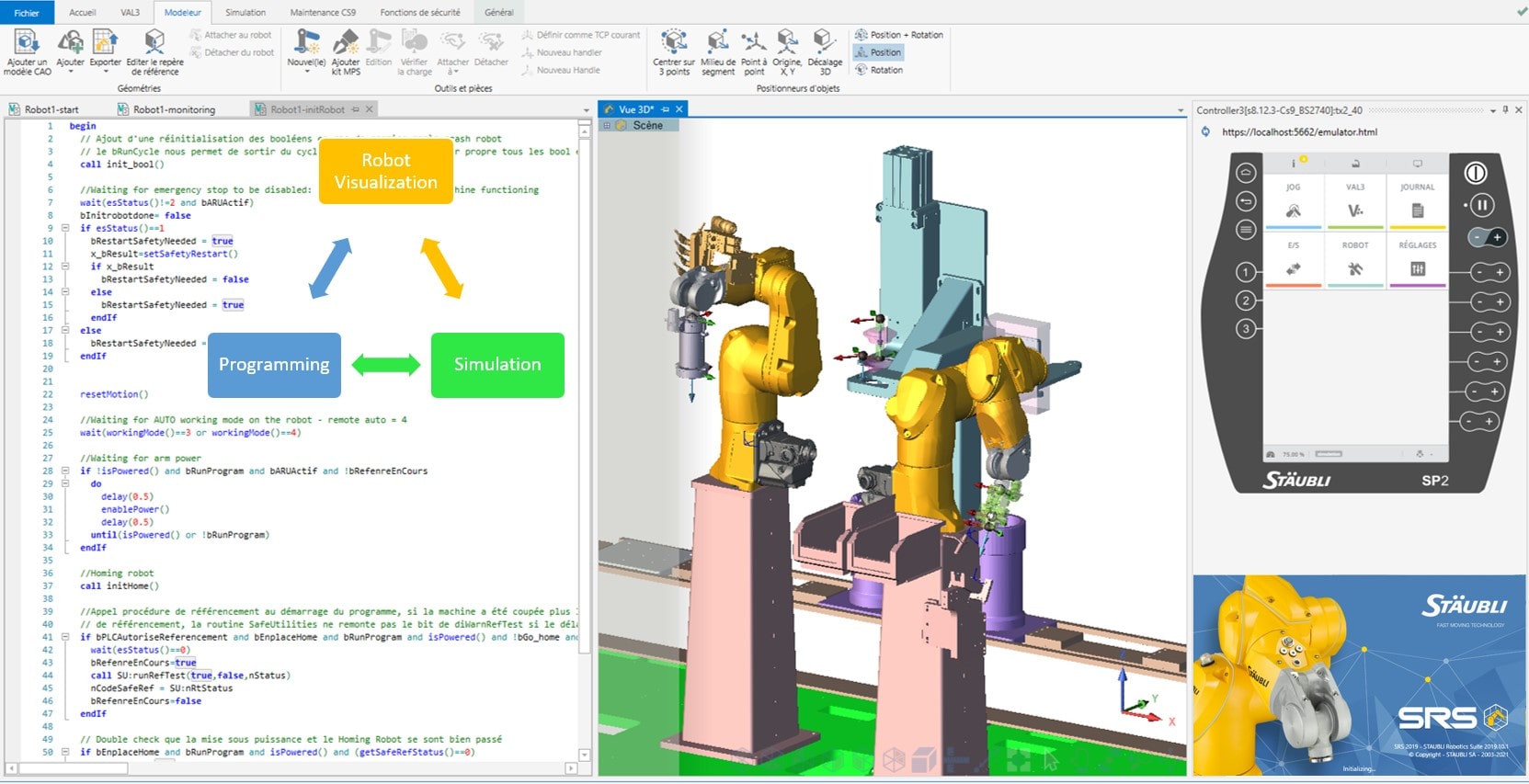
“Our open-mindedness allows us to explore the possibility of training ourselves in the use and programming via software from other robot manufacturers.”
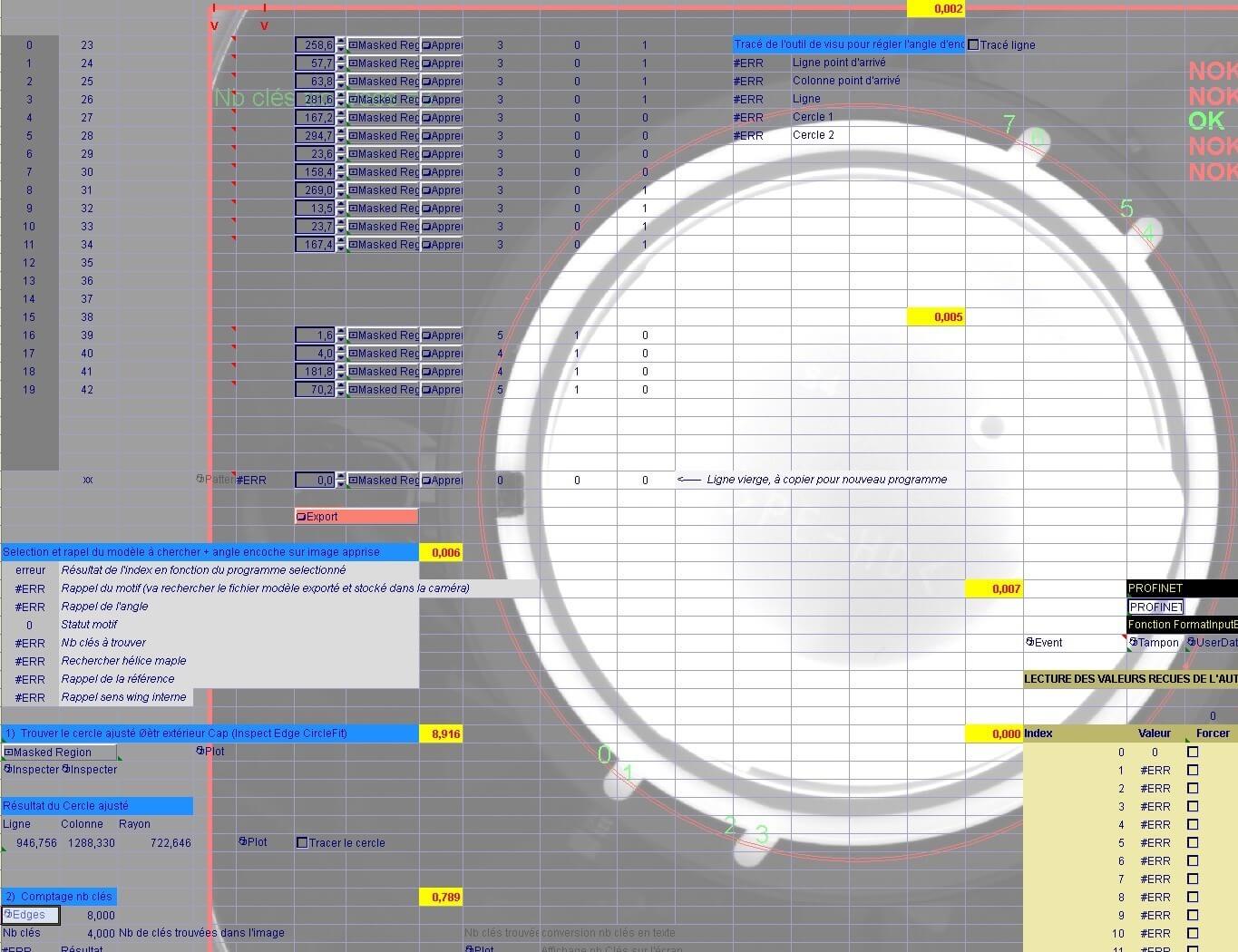
Other software / Utilities:
- TopSolid ERP: Management of business, orders, supplies, stocks, invoicing, etc.
- SafeExpert: Risk assessment software, risk analysis, compliance with the machinery directive
- Sistema : assessment of the required performance level (PLR, security)
- Adobe Premiere Pro : Video production and editing
- Programming software for machine vision cameras
What is 3D modelling?
3D modeling consists of digitally creating, using software, all kinds of parts, shapes, environments, buildings, objects, assemblies, machines, etc. in 3 dimensions, that is to say in volume. The goal is to visualize, animate, create simulations, but also to manufacture the parts from these designs, called 3D models.
These creation techniques use specialized computer software to achieve the desired result. Through successive stages of drawing, design and construction by adding and removing volumes, the components are created in the software. Their shape is defined, their material, their geometries. Their dimensions and visual rendering also. Then the unit components are assembled digitally, in a rigid or articulated way to allow movements according to the degrees of freedom left.
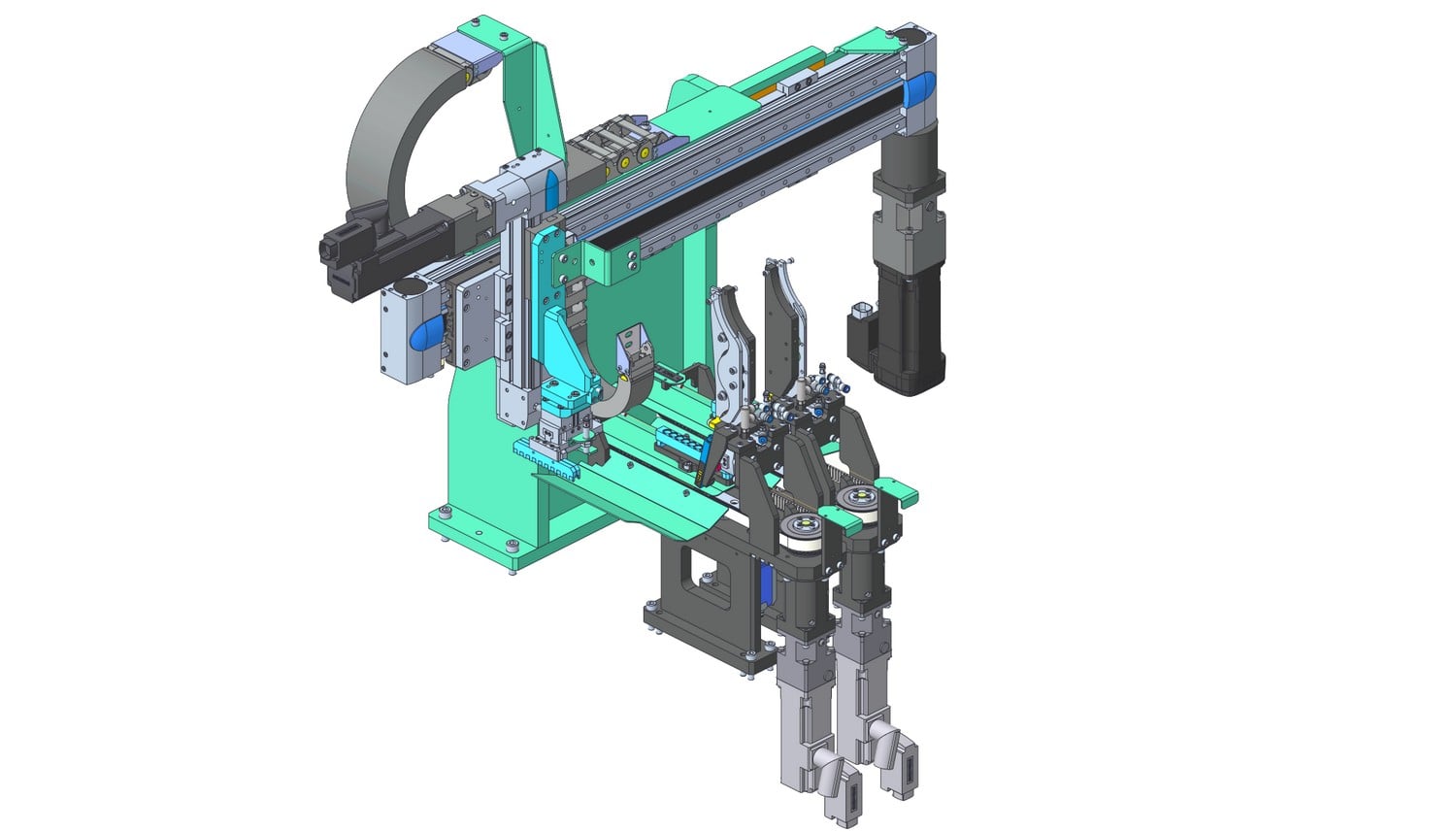
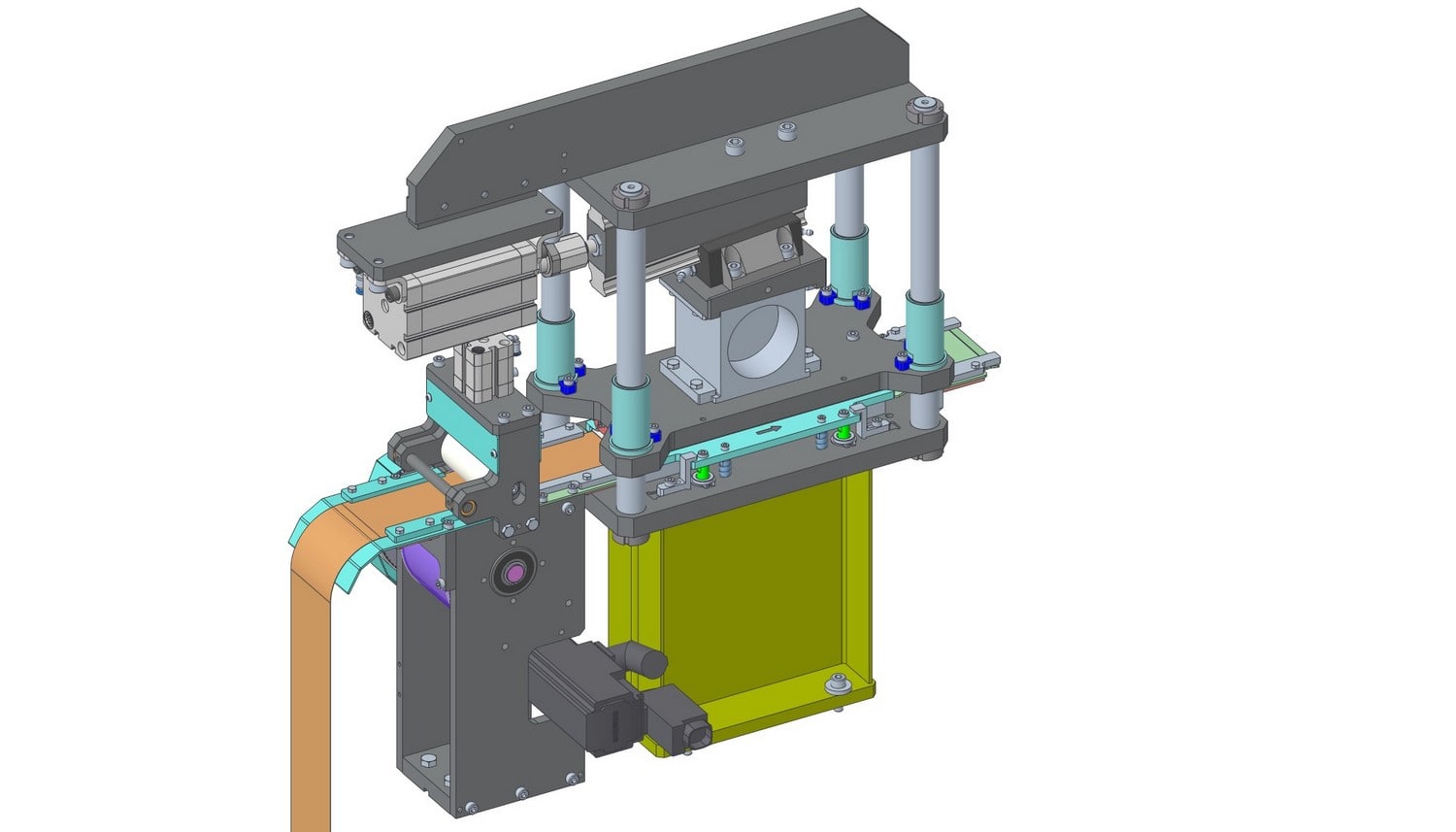
Modeling? To what purpose?
3D modeling is used in many fields such as the creation of objects, products or equipment. It allows the illustration of a concept, the development of engineering solutions, the detail of the construction of a product.
These techniques are also used to create visual renderings of products, places, or people even though they do not exist, or do not yet exist.
3D modeling and design of products and equipment
Le Sur-Mesure Industriel uses modeling techniques for the design and manufacture of parts, equipment, tools and machines and their digital simulation. For this, we use different professional CAD (Computer Aided Design) or simulation software (Mechanics and Robotics).
Concept illustration
In our profession as machine designers and builders, we use modeling tools daily to bring your projects to life.
From the beginning, to illustrate a concept, a principle, an idea, we schematically design the mechanisms, the strokes, the dimensions, etc. This stage allows us to outline the projects, to present the technical solutions envisaged for the requested function and to constitute documents on which our quotes are based.
Let us know your design needs.
Detailed design
We use 3D models to create, first digitally in the software, the different parts in their smallest details.
We detail each component of an assembly. Through the precise modeling of each part, we answer all the questions of definition of the part: geometries, functional interfaces with the other components, resistance, material, coating. We also integrate in this phase the constraints related to the means of obtaining, manufacturing.
These finished 3D models make assembly creation processes more reliable because all geometries and components are precisely defined. We also digitally validate all the functionalities of the equipment created. We take care to anticipate and facilitate future concrete operations to be carried out on the assemblies created: assembly to assemble and transport the equipment, disassembly and accessibility for maintenance and of course ergonomics in use.
You can benefit from our design approach by sharing your projects with us.
Digital simulation
Built from CAD models, 3D simulation of mechanisms has the advantage of setting the moving parts of an assembly in motion. This allows, for example, to check the travel of the different movements while validating, in the software, the absence of collision or interference between the parts and subassemblies created.
Thanks to these validation steps during the study phases, the production and development of equipment is largely made more reliable. Indeed, it is much preferable and much more economical to correct an error at the design stage, rather than when the parts are already produced. Modifying parts or components on CAD is flexible, fast, without any aesthetic impact and sustainable over time because the manufacturing drawings are up to date. Conversely, modifying a part in the workshop takes more time, requires working with the limits of the existing, impacts the aesthetics of the parts and leads to differences between the plan and the actual part.
The digital simulation of robot movements is also built from 3D models. This allows to program and visualize their complete work sequence, in their environment. You will find more details on this subject in our section dedicated to robotics.
See also: Other digital simulations
Advantages of modelling tools
Rapid, scalable, customizable development
With digital tools, repetitive tasks are automated and made easier. Certain verification tools help us to guarantee the precision of the parts we create.
These tools also enable us to create and manage manufacturing documents in an associative way. For example, a drawing document associated with a 3D model will be linked to and evolve synchronously with the 3D document.
The synchronised creation of bills of materials and detail and assembly drawings are powerful tools for rapid, scalable design.
Thanks to parametric construction functions, a 3D model can evolve rapidly by modifying the desired dimensions, or by adding or removing construction operations. The rest of the model updates and adapts to these new modifications. This greatly speeds up the duplication of parts, the creation of variants, the search for the best design and updating.
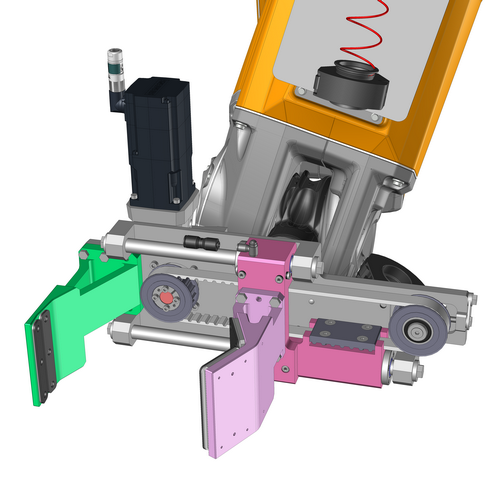
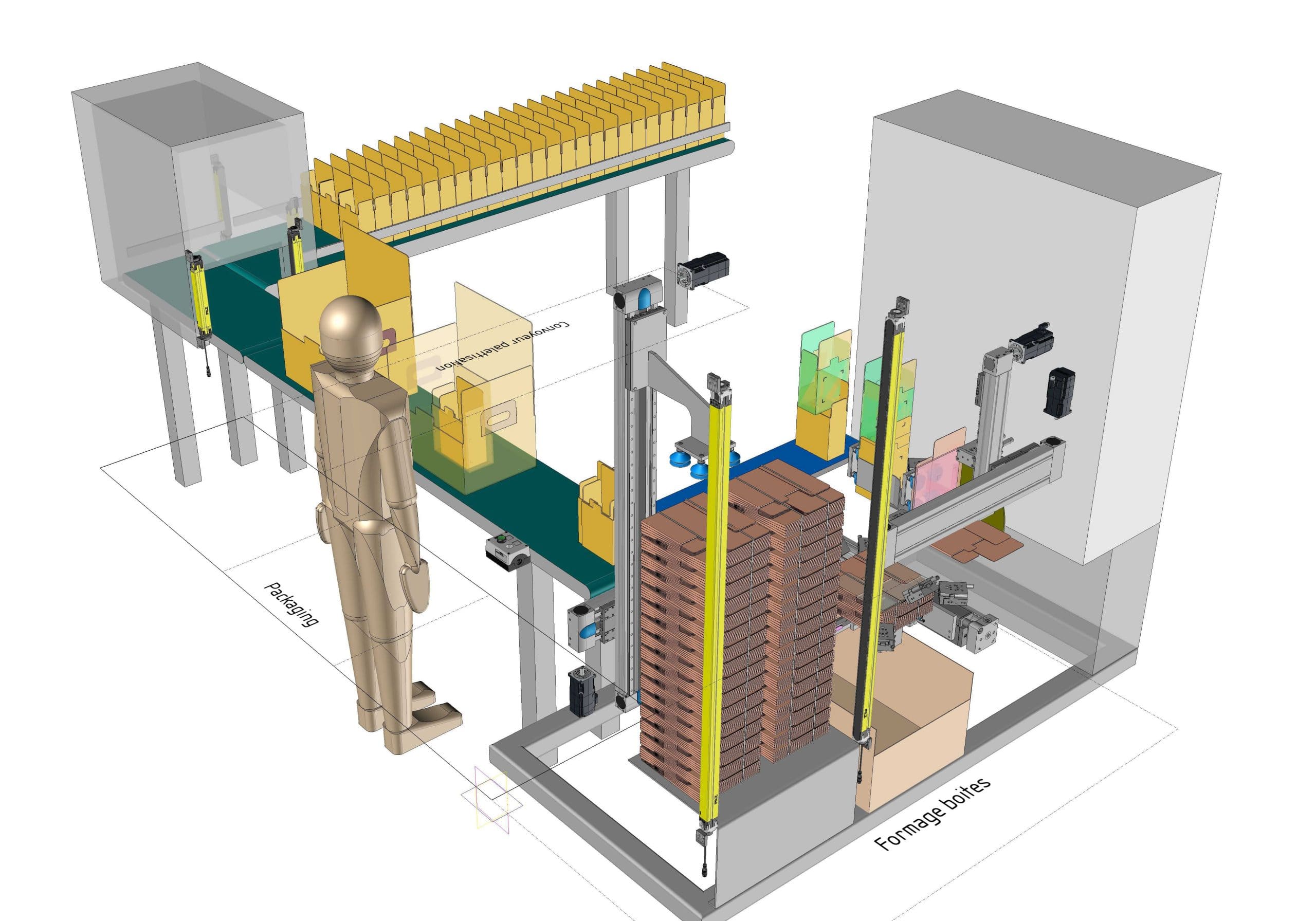
Visual communication
It is interesting to visualize the elements in order to project oneself into the various issues related to the development of any project. Visual aspect of the product or equipment, use, accessibility, handling, size, weight, ergonomics, etc.
3D models are excellent communication media between the various internal departments of our design office, but especially with our clients’ teams, to validate the concepts, functionalities and constitution of the equipment throughout the study phase during meetings for example. Indeed, we very often present the digital models during video meetings with our clients, thanks to screen sharing for example.
We are also equipped with our design software on the laptops used on the move, thus making it possible to project and share the models during on-site meetings.
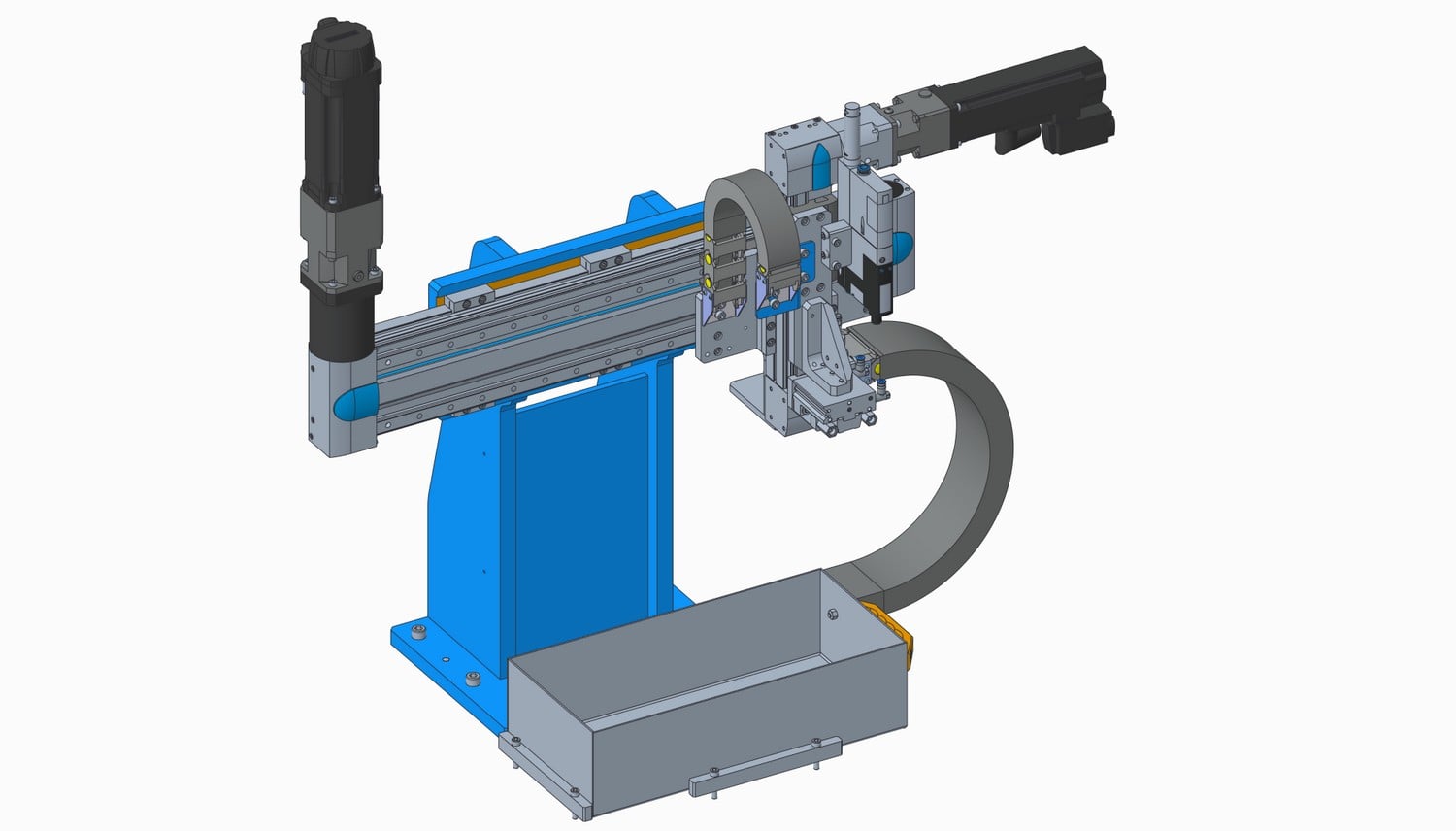
Link between models and achievements
CAD and manufacturing
In the majority of cases, our design office uses CAD models for the study and design stage prior to the manufacture and production of equipment, machines, tools, etc.
These two steps are closely linked: design anticipates manufacturing, manufacturing complies with the toleranced 2D detail drawings, resulting from the design. It is also very common for manufacturing to rely directly on 3D files. In sheet metal, for example, our subcontractors use the 3D files that we provide them to prepare the unfolded shapes, useful for cutting and folding parts. The use of 3D models by CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software also makes it possible to create machining programs using the 3D files that we produce.
3D Modelling for Prototyping
3D modeling also allows the creation of parts via 3D printing techniques. Indeed, from the digitally created 3D model, it is possible to generate files for additive manufacturing. Thus, parts, even very complex ones, can be manufactured quickly in order to validate their design, their geometries, their functions.
“Our design office is at your service to model your parts and products and support you until the delivery of functional prototypes.”
Surveys and modelling of existing conditions
Use of our software directly on site
We also use 3D modeling techniques to analyse existing equipment or an environment. To do this, we carry out a precise and careful geometric and dimensional survey of a machine, for example.
Our laptops equipped with design software also allow us to offer dimensional survey and modeling services for machines or environments live on our customers' sites. This allows us to digitally recreate the 3D model of the existing equipment in order to analyse it, transform it, develop it, add features to it, while taking into account the existing system. This method then accelerates developments, updates, and transformations since the checks and new designs are based on the digital data of the CAD model.
Using advanced survey software
This can be very useful for carrying out work in dense environments (piping, metal framework, compact installations, custom work adapted to existing installations, etc.). This makes it possible to make the addition of equipment, maintenance work and replacement of parts more reliable by relying on the data collected.